Figure 1 is the result of the above calculation method based on the sintering machine No. 3 of a sintering plant in China.

q' 7 series sinter residual carbon chemical loss, this example is not calculated.
Required for (1) sintering heat produced mainly from the ignition and combustion of solid fuels of coal gas. It accounts for about 84% of the heat income, in addition to the heat of oxidation of the raw materials during the sintering process. The plant is due to the use of magnetic iron ore and sulphide, which released a considerable amount of heat. For factories that burn hematite, this heat is very small. The British steel company Redcar sinter plant has the lowest solid fuel consumption in the world, with a dry coke consumption of only 37.5 kg per ton of sinter. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that the heating of solid fuel only accounts for 67% of the total heat income, while the iron-containing waste of steel mills such as rolled steel and broken iron reaches 14%, which greatly exceeds the ignition gas. Heating. Therefore, in order to save solid fuel, as much as possible, a large amount of exothermic iron-containing waste in the plant should be added to the sinter.

(2) The largest heat expenditure is the physical heat of the sinter, in addition to the physical heat of the exhaust gas and the chemical heat of incomplete combustion. The three sums accounted for 62.8% of the total heat, and a part of the residual heat of the sinter physical heat could be recovered by the cooler, but most of it was discarded. If the structure of the chiller is improved and a blast ring cooler is used, a preheated wind with a higher temperature can be obtained for preheating the combustion air or generating steam for power generation. The temperature of the flue gas is too low to utilize its physical heat. At present, some advanced countries use low-temperature volatile substances as a medium to recover heat for power generation or steam production. From this example, the proportion of chemical heat incomplete combustion is also high, accounting for 15% of the total heat, which may be due to insufficient combustion or excessive fueling. The solution is to improve the permeability of the layer.
1985, Sumitomo Heavy Industries, Ltd. and Sumitomo Metal jointly developed by the exhaust gas waste heat recovery efficiency of the full cycle technology, in Wakayama Steel N04 cool the sintering machine applied. Fig. 3 is a flow chart showing the cycle of sintering of the sintering waste gas of the machine. Figure 4 shows a representative thermal balance of the machine.


The combustion heat of coke powder, blast furnace ash and ignition fuel accounts for most of the heat supply, and its calorific value is 134 million joules, ton of sinter. The most heat-consuming is the unrecoverable heat of reaction of limestone decomposition and water evaporation, accounting for about 36%. The heat loss from the finished sinter, trolley and purlin is about 24%. The heat of exhaust gas such as sintering waste gas and dust removal gas It is reduced to 13%. The reason is that the latter-stage sintering exhaust gas and the cooling exhaust gas are circulated, and only the exhaust gas in the front stage of the sintering is discharged into the atmosphere. The heat dissipated from the wind and air ducts accounts for about 4%. The heat recovered from the waste heat boiler is the remaining 23%. Compared with the conventional waste heat recovered from the sintering waste gas and the cooled exhaust gas, the waste heat recovery amount of the No. 4 sintering machine is remarkably improved.
(3) The heat of evaporation of water and the heat of decomposition of carbonate also account for a large proportion. Maintaining the optimum state of moisture and strictly controlling water are of great significance for energy conservation. Low water operation is currently advocated. The automatic control of moisture is to reduce this part of energy consumption and improve the quality of sinter production. The heat of decomposition of carbonate is related to the alkalinity of minerals and sinter. Spinel or limonite is sintered, the heat consumption of decomposition is large, and fuel consumption is large, so the heat expenditure is also large. High alkalinity sinter requires more heat of decomposition, but because of the lower melting point of the calcium ferrite binder phase, high alkalinity sinter does not require much heat.
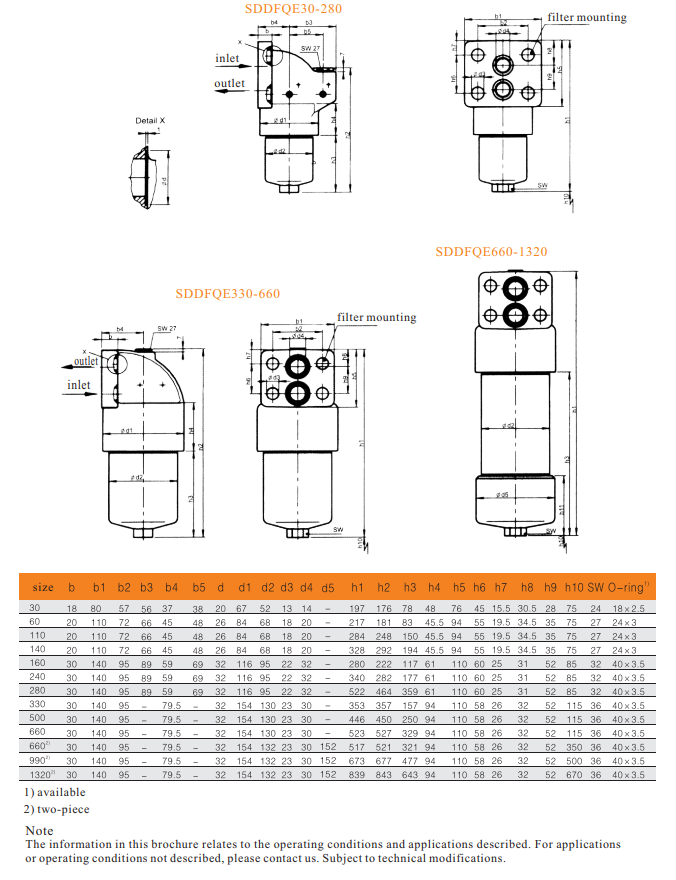
SDDF QE series pressure filters are designed in accordance with international regulation, which consist of a Filter Housing with a screw on cover plate.
Standard equipment
-mounting holes in the filter head
-two-piece bowl for size 660 and above
-compatibility with fire-resistant fluids HFA/HFC
-drain plug with pressure relief(size 330 and above)
Connection Diagram
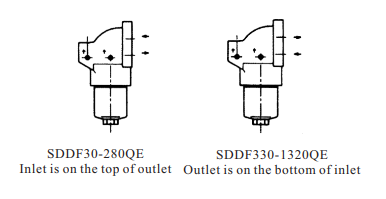
Shengda is sure that our filters are of reliable performance so that they can protect hydraulic parts from polluting and machines from abrasion.
Filter elements are available with the following pressure stability values
BN/HC:25bar
BH/HC:210bar
W/HC:30bar
V:210bar
Seals
-NBR(=NBR)
Special models and accessories
-with bypass valve
-drain plug with pressure relief
-seals in FPM, EPDM
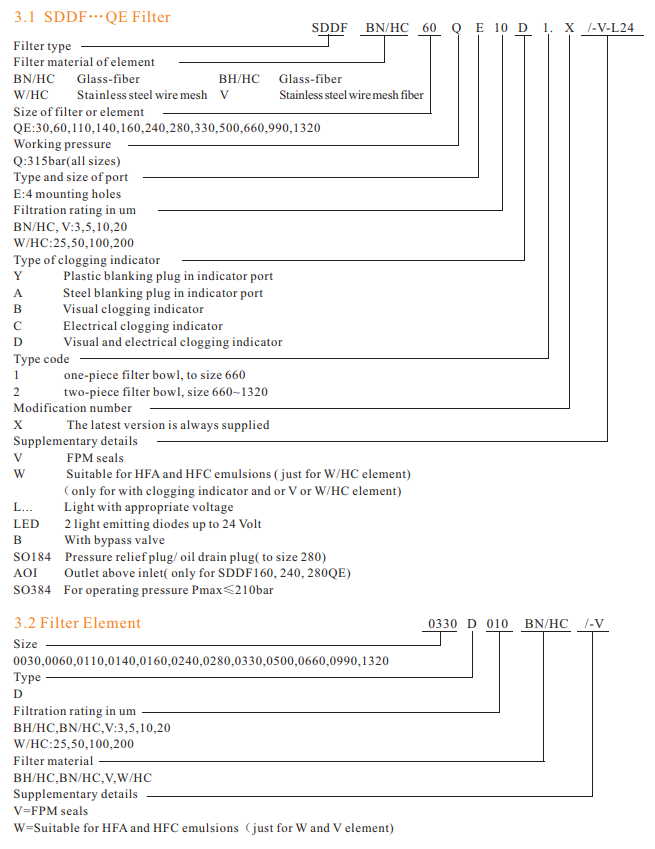
Flange-Mounted Pressure Filter
Grader Filter,High Pressure Filter,Flange-Mounted High Pressure Filter,Flange-Mounted Pressure Filter
Xinxiang Shengda Filtration Technique Co., Ltd. , https://www.shengdafiltration.com