Effects of Winter Wheat Genotype, Environment, Year and Its Interactions on Variety Gluten Index
The effects of winter wheat genotype, environment, year, and their interactions on the gluten index of the wheat cultivars were used to determine the effect of various influencing factors on the gluten index and analyze the variance. The results showed that the interaction of year, environment, genotype and each factor had extremely significant (P<0.01) effect on the gluten index of wheat. Among the independent effects of various factors, the genotype was the largest in mean square, accounting for 46.24% of the total variance, far greater than the annual mean square (7.95%) and environmental mean square (1.47%), indicating that wheat gluten index is mainly independent of gene expression. Impact; Among the effects of interaction effects on gluten index, the effect of year × genotype interaction was the largest, accounting for 33.83% of the total variance, and the gene × environment interaction was the smallest, accounting for 1.83% of the total variance, indicating that the gluten index was affected. Genotype and year interaction effects are greater. Jing Qi [7-8] also found that genotypic differences in wheat grain quality traits are different under different environmental conditions, and gluten index gene expression is less affected by the environment and can be modified by genetic recombination.
Correlation between gluten index and quality characteristics
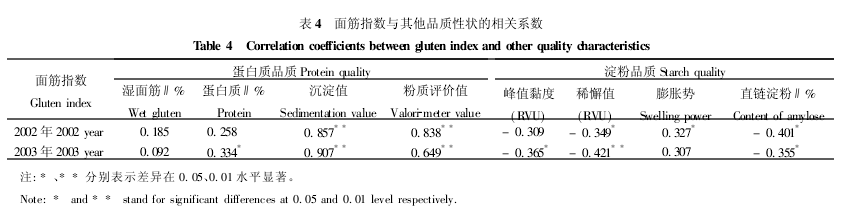
It can be seen from Table 4 that the degree of correlation between the gluten index and the grain quality traits of eight wheat varieties varies with different traits. In protein quality, all indicators were positively correlated with gluten index, among which the correlations between sedimentation value, silty evaluation value and gluten index reached a very significant level; while gluten index had no significant correlation with protein content and wet gluten content. In comparison, the correlation coefficient between protein content and gluten index was greater than that of wet gluten and reached a significant level in 2003 (R=0.334). This shows that the protein, gluten content, and gluten quality in wheat flour are different concepts. The content of protein and gluten are only quantitative traits, which does not reflect the quality of the wheat flour. The gluten index is significantly positively correlated with the evaluation value of silty gluten. Therefore, using gluten index to measure gluten quality of wheat flour, so as to comprehensively evaluate the quality of wheat flour not only has its significance, but also has its practical value.
In the starch quality, the peak viscosity, the dilute value, the amylose content and the gluten index were negatively correlated. Except for the peak viscosity in 2002, all Other indicators reached significant levels. It shows that with the increase of starch gelatinization characteristics and the increase of amylose, the gluten index has a decreasing trend. In breeding, the aim of reducing the proportion of amylose in starch is the purpose; the swelling potential is positively related to it, and in 2002 The annual level reached significant level (R=0.327), indicating that the material with larger expansion potential has higher gluten index. In high-quality breeding, the higher expansion potential should be taken as an important indicator, which is related to the aforementioned low amylose content. As a selection indicator is consistent.
Experiments and Discussions on the Relationship between Wheat Gluten Index and Wheat Genotype by Gluten Indices Tester The interaction between genotype and environment is the interaction between biological characteristics and natural laws. It has wide adaptability or special adaptation to adverse environment. Sex varieties are of great significance. The study showed that all the influencing factors of the gluten index reached the extremely significant level, and the genotype effect was the most obvious; among the interaction effects, the year × genotype interaction effect was the most obvious. For the gluten index, PH1521 is the highest, and has the smallest change between locations and years, and is a good breed. At the same time, we can see that the Tengzhou pilot has a higher gluten index, but in the 2002 and 2003 two years, the quality changes greatly, and the stability is poor. Therefore, the conclusion that this area is a high gluten zone cannot be obtained based on the results of the two years. Based on years of experiments to determine the appropriate cultivation area of ​​the variety. In summary, the environment and genotypes affect the gluten index, but the gluten index is mainly affected by genotypes; the gluten index varies greatly among different varieties. Therefore, it is feasible to improve the quality of wheat gluten through genetic breeding, and the selection of varieties and regions of high gluten index through experimentation will give full play to the advantages of local environmental resources and the use of favorable genotype and environment interaction effects to maximize the variety. High quality potential has important theoretical and practical significance. Studies have shown that baking quality has no significant correlation with protein and gluten content, but has a significant positive correlation with gluten quality. The results of this study indicate that the wheat gluten index is significantly correlated with sedimentation value and silty evaluation value, but not with protein and wet gluten. This is similar to previous studies. The study also found that gluten index and most starch quality There was a significant negative correlation, but there was a positive correlation with the swelling potential. Therefore, current quality breeding should focus on improving the quality of gluten on the basis of certain protein content, gluten index is an important indicator of wheat quality improvement, and high gluten index varieties should be selected during the breeding process. In the process of high-quality wheat production, comprehensive consideration should be given to the interannual variation of climate conditions in varieties, locations, and regions. In the process of wheat promotion, it is necessary to make rational use of local natural conditions and comprehensively consider the influence of genotype and environment on wheat quality. The gluten index has high heritability and can be used for the screening of a large number of strains in the early generation. It is an effective quality inspection method.
Related Instruments: Electronic Container New International Powder Inspection Germplasm Resource Library
Kids Stacking Cups,Stackable Cups Game,Stackable Plastic Cups,Plastic Stacking Cups
Ningbo Gibbon Sports Culture Co.,Ltd , https://www.gibbonsports.com